Introduction of Computer
Introduction of Computer
Computers are basic devices for modern life and are also necessary for a wide range of industries.
Types of computer
There are two bases on which we can define the types of computers. We will discuss the type of computers on the basis of size and data handling capabilities
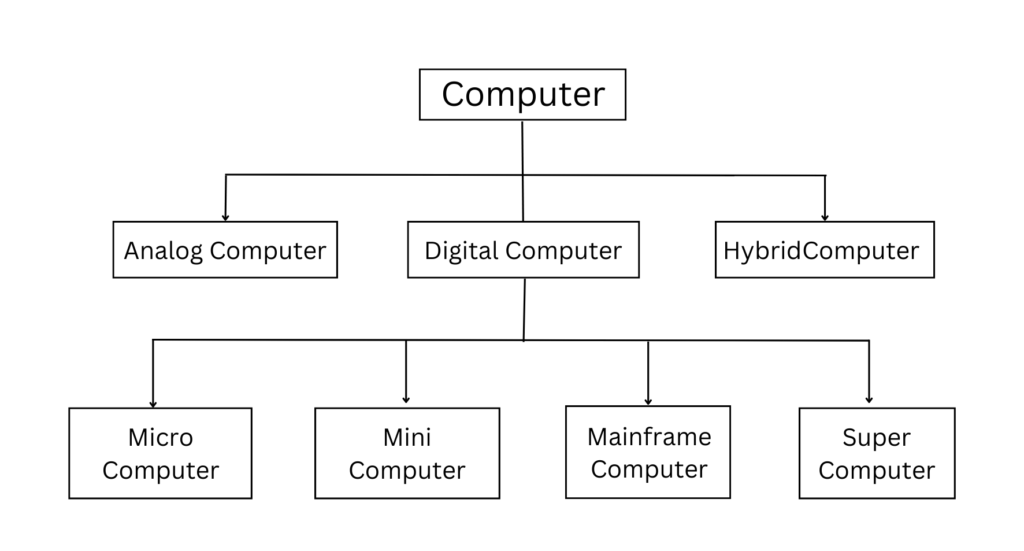
Computers are mainly categorized into three types
- Analog Computers
- Digital Computers
- Hybrid Computers
1. Analog Computer
Analog computers calculate continuous data using physical qualities such as voltage and current, making them perfect for analytical-based exercises, engineering, and control systems.
Here are some of the examples –

Speedometer

Thermometer

Voltmeter

Seismograph
2. Digital Computer
A digital computer processes separate information by calculating with binary digits (0s and 1s) and is commonly utilized in modern computing for a wide range of activities requiring accuracy and flexibility.
- The Microcomputer
- Mini Computer
- mainframe computer
- The Supercomputer
2.1 The Micro Computer
Examples of Microcomputer –

Desktop

Mobile

Laptop

Gaming Console
2.2 Mini Computer
Examples of Minicomputers are – CII Mitra 15, IBM midrange computers, Hewlett-Packard HP 3000 series and HP 2100 series etc.

2.3 Mainframe Computer
Examples of Mainframe computers are – IBM z16, IBM System z9, HITAC S-3800


2.4 Super Computer
Note – India’s first supercomputer is PARAM 8000.
Examples of Supercomputers – Frontier, PARAM 8000, CDC 6600, IBM 7030, etc.

3. Hybrid Computer
A hybrid computer combines analog and digital computer abilities collecting continuous data through analog components and performing complicated calculations through digital components, making it suitable for specific scientific and commercial uses.
Here are some of the examples of Hybrid Computers –

Pump

ECG Machine

CT Scan

Ultra Sound Machine
Charecterstics of computers
Computer and Latest IT Gadgets
The latest IT items, such as modern smartphones, tablets, wearable technology, virtual reality devices, and smart home technologies, make everyday life easier.
Evolution of computer and its application
Computers have changed from as big mechanical devices to small but powerful devices. PCs made them smaller, and the internet connected across the world. Today, computers are used mostly in science, banking, health care, and entertainment. Because of the ways in which AI, IoT, and technology have changed daily life, technology is now important.
Generation of computer
Based on the level of technical development, the evolution of modern computers has been divided into multiple periods known as computer generations.
Hardware
There are two types of Hardware
1. Internal Hardware
Parts which are installed inside the case of a computer, Internal hardware components are essential to the operation of a computer. such as RAM, Processor, SMPS, Mother board etc.
2. External Hardware
Hardware that is used outside the case of a computer, usually known as peripheral devices some of them are used for input some for output. such as a Keyboard, Mouse, Monitor, etc.
Software
When the user only connects with software, the software offers understanding to the device. It is a collection of computer data and instructions. It is divided into two categories: System Software, which provides the computer’s important non-task-specific functions, and Application Software, which is used by users to do specific tasks.
Some Types Of Software:
- Application Software
- System Software
- Utility Software
- Mobile Apps
- Open Source and Proprietary Software
1. Application Software
Examples – MS Word, Teams, Google Chrome, Video Editor, etc.
2. System Software
Example – Microsoft Windows, Linux, Android, Device Drivers.
3. Utility Software
Example- Disk Clean up, Firewall, Network, System Diagnosis.
4. Mobile Apps
Examples- Digi Locker, My Gov Umang App Arogya Setu App.




5. Open Source Software
Example – LibraCalc, LibraWritter, VLC, Linux, Mozilla Firefox
Central Processing Unit
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the main part of a computer which is responsible for doing calculations and receiving instructions. It works like the “brain” of the computer. it collects data from memory and controls the other parts. The speed and performance of the CPU play an important role in a computer’s performance.
A CPU has three parts:
- Arithmetic Logic Unit
- Central Unit
- Memory Unit

1. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Does addition, subtraction, multiplication, and comparison calculations, in addition to many other logical calculations.
2. Central Unit (CU)
Controls the flow of instructions by collecting them from memory, processing them, and arranging data transfer both within and outside the CPU.
3. Memory Unit (MU)
The storage device maintains its data even when the power is switched off. It includes magnetic hard drives, flash memory SSDs, optical drives (CD/DVD), USB drives, memory cards, and magnetic tapes. HDDs, flash memory SSDs, optical drives (CD/DVD), USB drives, memory cards, and magnetic tapes are all examples of hard disc drives.
Input Devices
Input devices provide data and instructions to computers. Examples include keyboards for typing, mouse for pointing and clicking, touchscreens for finger input, scanners for document digitalization, and microphones for voice instructions.
Output Devices
On output devices, the user receives processed data. Other examples of output devices include projectors for larger presentations, audio speakers, printers for hard copies, headphones for private sound, and graphical monitors.